|
| ▲cooking fumes generated during cooking (Source: pxhere) |
For those planning outings in spring and autumn, there's always something to check: the outdoor fine dust index. Fine dust refers to extremely small dust particles that are not visible to the naked eye, formed by reactions of various pollutants in the air emitted during processes such as factory operations or burning fuel from automobile usage. The Ministry of Environment warns, "Because fine dust particles are very small, they are not filtered out by the nasal mucosa, and long- term and continuous exposure can lead to various diseases such as asthma, pulmonary diseases, and cardiovascular diseases." However, what many people overlook is the danger of indoor fine dust generated during cooking, known as cooking fumes. The most significant cause of indoor air pollutants is harmful substances generated during cooking, such as ultrafine dust, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, and the like.
Cooking fumes are smoke generated when frying food using hot oil, and it contains various components that decompose during the process, taking the form of ultrafine particles (PM2.5). According to a study by Crouse Dan et al. from Canada in 2019, the association between PM2.5 and lung cancer is greater than other harmful substances, indicating a significant contribution to increased mortality rates. In fact, the International Agency for Research on Cancer designates cooking fumes as a carcinogen (2B), and the Korean Association for Lung Cancer announced that over 85% of female lung cancer patients in Korea are non- smokers. Still, their lung cancer differs in form from that caused by smoking, such as squamous cell carcinoma or small cell carcinoma, highlighting the risk of cooking fumes.
The WHO announced that annually 3.2 million people die from household air pollution caused by cooking fuels. The degree of pollutant generation also varies depending on the type of fuel and cooking method. According to data released by the National Institute of Environmental Research in 2013, the concentration of indoor ultrafine dust (PM2.5) before cooking was 60㎛/㎥, while it increased to 119㎛/㎥ when boiling food, 878㎛/ ㎥ when roasting, and 269 ㎛/㎥ when frying. These values exceed the Ministry of Environment's ultrafine dust, 'very bad,' standard of 76㎍/㎥.
With the increasing trend of studies on the causal relationship between cooking fumes and lung cancer, in 2019, the Korea Occupational Safety and Health Research Institute released a report titled, "Hazard Levels of Cooking Fumes in Republic of Korea Schools." The research team, which surveyed 24 school kitchens, stated, "In the evaluation of the occurrence form of fine particles PM2.5 and PM10, some cooking environments exceeded indoor air quality management standards, carbon monoxide exceeded the short- term exposure limit of 200ppm in some cooking processes, and the instantaneous emission of carbon dioxide increased to a high concentration of over 8,888ppm, confirming the possibility of intoxication through chemical asphyxiants and simple asphyxiants compound action." Due to such reasons, despite working as a cook for 15 years, a woman was diagnosed with lung cancer in 2019 despite being a non- smoker. Subsequently, her lung cancer was recognized to have a causal relationship with cooking fumes, and in February 2021, she became the first school cook to be approved for occupational lung cancer coverage. However, despite such tragic incidents, in March 2023, there were cases of 31 school kitchen workers nationwide being diagnosed with lung cancer collectively. Following this, members of the nationwide non- regular workers' union of schools staged a protest demanding countermeasures.
Then, what are the methods to prevent harmful substances generated during cooking? The most important method is active ventilation, such as opening windows and using mechanical ventilation devices like ventilation hoods during cooking, located above the stove. Mechanical devices like hoods can reduce harmful substances by about two- thirds. According to inspection results conducted by education offices after the collective lung cancer diagnosis cases, it was revealed that 97% of 4,800 schools lacked proper ventilation equipment such as hoods. Using mechanical devices like hoods can reduce harmful substances by about two- thirds. Additionally, using an air fryer instead of frying pans or cooking by boiling or steaming can also help reduce indoor fine dust emissions. Since cooking fumes are invisible threats to our health, it is essential to be aware of their risks and strive for a healthy lifestyle through proactive prevention efforts.
By Kim Min-seong, reporter kms9494274@gmail.com
<저작권자 © The Campus Journal, 무단 전재 및 재배포 금지>
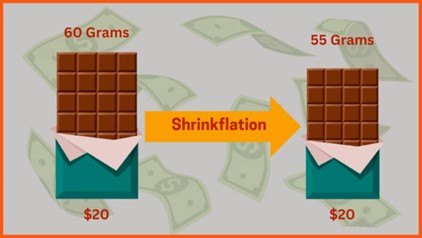 Shrinkflation, Consumer Deception
Shrinkflation, Consumer Deception